For proving my point of the impact of sports on mental health I read a scientific review called “The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model“ which was conducted by Narelle Eather, Levi Wade, Aurélie Pankowiak and Rochelle Eime in 2023. The review screened studies that were published between 2012 and March 2020 to find out the relation between sport participation and mental health and social outcomes.
This is how the term mental health is defined in the review:
According to the World Health Organization, mental health refers to a state of well-being and effective functioning in which an individual realizes his or her own abilities, is resilient to the stresses of life, and is able to make a positive contribution to his or her community. Mental health covers three main components, including psychological, emotional and social health. Further, psychological health has two distinct indicators, psychological well-being (e.g., selfesteem and quality of life) and psychological ill-being (e.g., pre-clinical psychological states such as psychological difficulties and high levels of stress). Emotional well-being describes how an individual feels about themselves (including life satisfaction, interest in life, loneliness, and happiness); and social well–being includes an individual’s contribution to, and integration in society.
The review showed that adults who participate in sport activities on a regular basis have better mental health conditions: there was shown to be a strong relation to psychological well-being, like e.g. higher self-esteem and life satisfaction, and lower psychological ill-being, like e.g. a lower level of depression, anxiety and stress. Furthermore, sports can have a positive influence on social factors such as improved self-control, pro-social behaviour, interpersonal communication anda sense of belonging. Although this review researched the impact of sports on adults, it can still provide useful insights for the topic of sports education in schools and can be transferred to youths.
Specific outcomes of the review
Another interesting finding is that the positive effects are not as strong when it comes to elite-level sport: in contrary to community sport it can cause higher levels of psychological distress. Research in this field indicates that this fact is related to the high mental and physical demands on pro-athletes. The effects of the pressure to perform prove my point of the negative impact that performance oriented sports education can have on the students mental well-being.
Summary of findings in the review:
- the positive effects of participating in sports even exceed the effects of other leisure-time activities or recreational activities
- the effects occur in all different kinds of sports and across different life stages and sub-populations
- there is a strong tendency for youths to drop out of community sports during adolescence, which leads to many people missing out on the positive effects of sports on mental well- being
- over the past 25 years there was a consistently high rate of around 10% of adults affected by mental illness
- especially among young adults there is a high level of loneliness and social isolation
- improved vitality through sport participation
- if adults participate in sports they chose themselves and that they enjoy, there is a relation between the intensity of the sports participation and the amount of mental health benefits
- social factor of sports (social support, peer bonding) as an explanation for the benefits on mental and social health
- evidence shows that participation in sports in adolescence and young adulthood prevent depression, anxiety and stress longterm
- aspects that impact the improvement of psychological well-being:
- psychological mechanisms: development of self-efficacy, opportunity for mastery, changes in self-perceptions, the development of independence, and for interaction with the environment
- behavioural mechanisms: changes in sleep duration, self-regulation and coping skills
- social mechanisms: social influence/social comparison; social control; role-based purpose and meaning (mattering); self-esteem; sense of control; belonging and companionship; and perceived support availability
- improved perception of capability or value (within a team) -> improved self-esteem
- self-efficacy: learning new skills, overcome challenges, self-control mastery -> confidence in the ability to cope with general life challenges
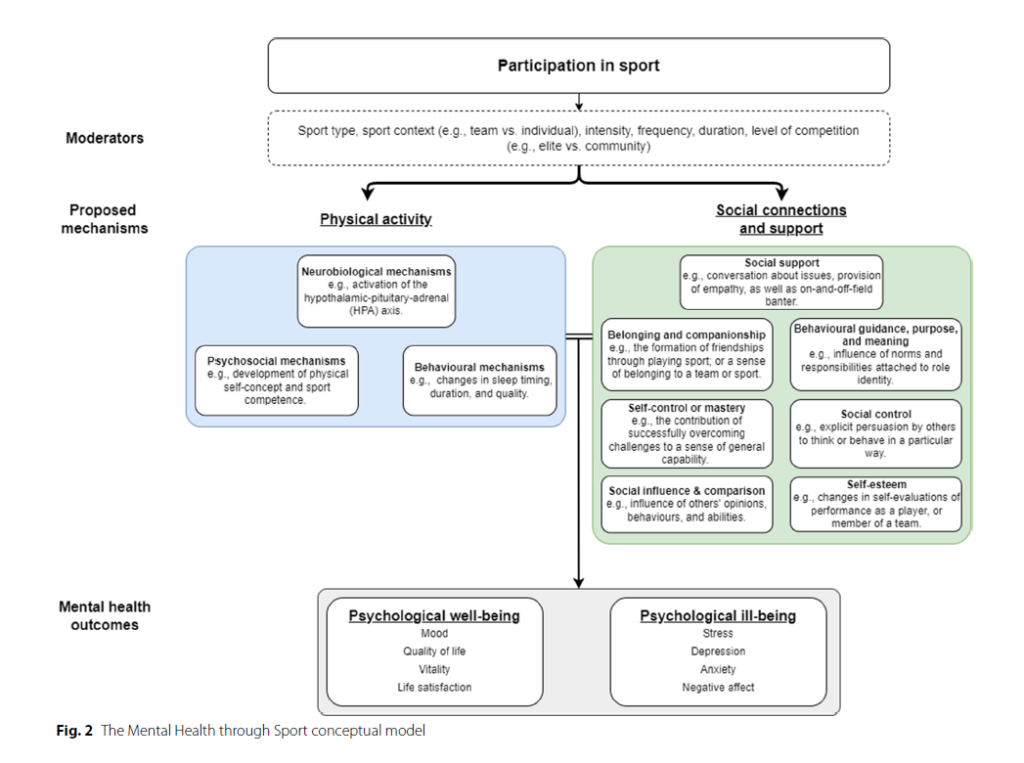
Deductions based on those findings:
- It is important that one has the possibility to choose sports that they enjoy
- Social bonding is an important factor for unfolding the potential of sports. If social bonding is prevented by performance pressure, unhealthy competition and comparison, the potential of sports can not be reached
- For students to learn new skills and experience self-efficacy and mastery, sports education needs to be tailored to the student’s individual capabilities and needs
Sources
Eather, Narelle; Wade, Levi; Pankowiak, Aurélie; Eime, Rochelle: The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model. 2023